Pregnancy Testing – Deep Dive into the Beta HCG Test
Pregnancy tests aim to provide a simple yet effective method of determining if you’re pregnant. There are two primary types of pregnancy tests available: urine tests and blood tests. While urine tests are more commonly used due to their convenience and over-the-counter availability, blood tests, specifically the Beta HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) test, offer a more detailed insight into the pregnancy. Here’s an in-depth look at the Beta HCG pregnancy test, how it differs from urine tests, its accuracy, uses, and how to interpret the results.
What is a Beta HCG Pregnancy Test?
A Beta HCG test is a blood test used to detect pregnancy. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone produced by the placenta after implantation. The beta subunit of HCG can be detected in the blood serum of expectant mothers approximately 11 days after conception; HCG can be detected in the urine 12-14 days after conception.
There are two types of HCG tests:
- Qualitative HCG test: This test simply detects the presence of HCG in the blood. It gives a “yes” or “no” answer to the question, “Are you pregnant?” Doctors often order this test to confirm pregnancy.
- Quantitative HCG test (Beta HCG): This test measures the specific level of HCG in the blood. It can detect even very low levels of HCG, making it a highly accurate test.
How Does a Beta HCG Test Differ from Urine Tests?
While both urine pregnancy tests and Beta HCG tests aim to detect the presence of HCG, there are distinct differences:
- Method of Testing: Urine tests can be done at home, while Beta HCG tests require a blood sample taken in a healthcare setting.
- Sensitivity: Beta HCG tests are more sensitive than urine tests and can detect lower levels of HCG. This means they can confirm pregnancy earlier than urine tests — typically around 11 days after conception.
- Information Provided: While urine tests only provide a positive or negative result, a Beta HCG test can provide more information about the pregnancy, like the approximate age of the fetus, or if there are potential complications.
The Accuracy of Beta HCG Pregnancy Test
Beta HCG tests are highly accurate. Because they can measure the exact amount of HCG in the blood, they can detect pregnancy earlier than urine tests, and they can also confirm or rule out potential problems.
However, while the Beta HCG test can detect if you’re pregnant, a single test can’t always accurately predict a healthy pregnancy. Levels of HCG can vary greatly among individuals, and a single measurement isn’t always indicative of a problem or complication. Doctors often will test HCG levels more than once, looking at how the levels change over time.
Uses of Beta HCG Pregnancy Test
Aside from confirming pregnancy, a Beta HCG test can be used for the following:
- Monitoring Pregnancy: Doctors may use Beta HCG tests to monitor the health of a pregnancy, particularly in the early weeks. They may use serial measurements to see if HCG levels are rising as they should.
- Identifying Ectopic Pregnancy: Lower than usual levels of HCG or levels that do not increase as they should may suggest an ectopic pregnancy — where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
- Screening for Down’s Syndrome: As part of the “double,” “triple,” or “quadruple” screen test, the Beta HCG test can help assess a baby’s risk of Down syndrome.
Interpreting Beta HCG Test Results
Interpreting Beta HCG test results isn’t always straightforward, as normal HCG levels can vary widely. Typically, in a healthy pregnancy, HCG levels double approximately every 48 hours in the first weeks following conception.
However, unusually high or low levels, or levels that don’t increase as they should, might indicate a problem, such as an ectopic pregnancy, a miscarriage, or a potential chromosomal abnormality. In such cases, your healthcare provider will likely order further tests to determine the cause of the abnormal HCG levels.
It’s important to remember that while the Beta HCG test is a crucial tool in pregnancy monitoring, it is just one aspect of a larger picture. It should be used in conjunction with other tests and examinations to ensure a comprehensive understanding of both maternal and fetal health.
In conclusion, the Beta HCG pregnancy test is a sensitive, accurate, and versatile tool in the early detection and monitoring of pregnancy. By understanding its uses and how to interpret the results, you can gain a more comprehensive view of your pregnancy journey.
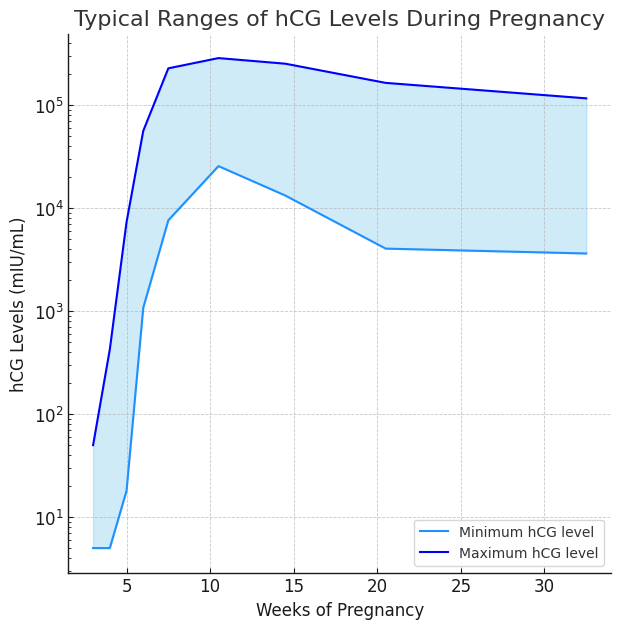
Here are typical ranges for hCG levels during pregnancy:
- 3 weeks: 5 – 50 mIU/mL
- 4 weeks: 5 – 426 mIU/mL
- 5 weeks: 18 – 7,340 mIU/mL
- 6 weeks: 1,080 – 56,500 mIU/mL
- 7 – 8 weeks: 7,650 – 229,000 mIU/mL
- 9 – 12 weeks: 25,700 – 288,000 mIU/mL
- 13 – 16 weeks: 13,300 – 254,000 mIU/mL
- 17 – 24 weeks: 4,060 – 165,400 mIU/mL
- 25 – 40 weeks: 3,640 – 117,000 mIU/mL
Looking to book a blood test with us? Please visit our Blood Tests page. If you already had your pregnancy confirmed, we recommend to book an early pregnancy scan to check for the baby’s wellbeing.