Spital Clinic GP Partnership

LPC x Spital Clinic Partnership
What You Need to Know about Spital Clinic GP
-
Published
-
Last Modified
Tags
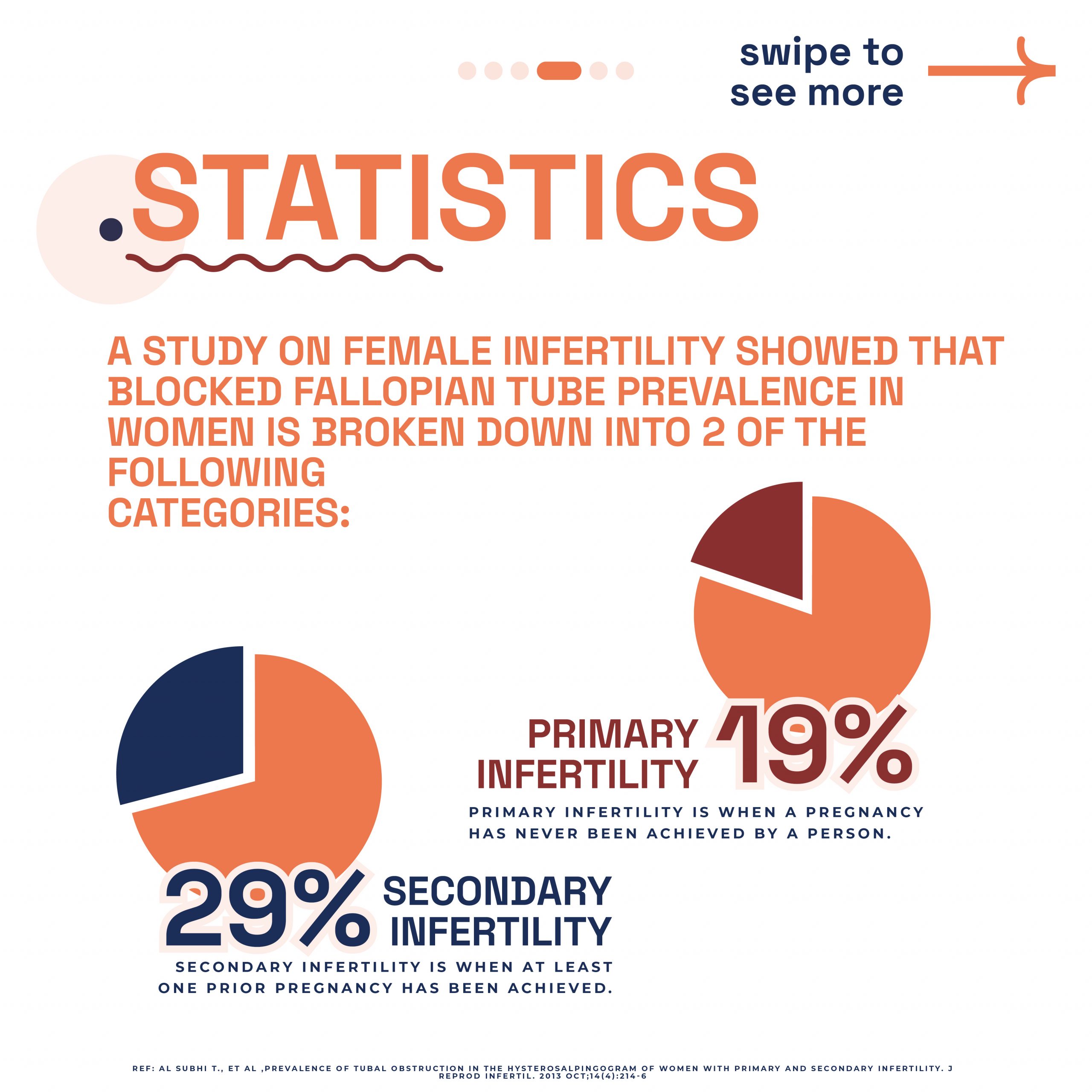
London Pregnancy Clinic proudly announces our partnership with the Spital Clinic GP. This collaboration enhances our holistic, high-quality healthcare services. Together, we provide comprehensive care that includes general practice, sexual health, and specialised women’s health services. This partnership ensures that our patients receive the best care possible, supported by experienced professionals and cutting-edge facilities. In this blog, we will explore the services offered at Spital Clinic and why this partnership is vital for our mission to deliver holistic healthcare.
We are excited to announce a new partnership between London Pregnancy Clinic and Spital Clinic, aimed at enhancing the quality of healthcare services we offer. This collaboration allows us to provide a broader range of medical services, ensuring our patients receive comprehensive care. From general practice to specialised women’s health services, our combined expertise guarantees top-tier healthcare for all.
Spital Clinic GP Services
Spital Clinic’s general practitioners (GPs) offer a variety of primary care services designed to address common medical conditions, manage chronic diseases, and promote overall health. The general practice services are comprehensive and tailored to meet each patient’s individual needs. They provide diagnosis and treatment for common medical conditions and offer referrals to specialists when needed, ensuring you receive the most appropriate care. Regular check-ups and health screenings help maintain your health and well-being.
Managing long-term conditions is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. Spital’s GPs work closely with patients to manage diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. Tailored treatment plans help you stay healthy and manage your condition effectively. Spital Clinic offers a full range of routine vaccinations and travel immunisations. Keeping up to date with vaccinations is essential for preventing disease and protecting your health. Spital Clinic GPs ensure that you receive the necessary vaccinations for your specific needs.
Spital Clinic can perform certain minor surgical procedures on-site, including skin tag removals and joint injections, providing quick and effective treatment without the need for a hospital visit. Preventive healthcare is a cornerstone of our services. Spital Clinic offers health checks, cancer screenings, and lifestyle counselling to help you maintain your health and prevent potential issues. Their GPs are dedicated to providing the best preventive care possible.
Reproductive Health
Sexual health is an important aspect of overall well-being. Spital Clinic provides comprehensive sexual health services in a confidential and supportive environment. Our team is committed to helping you maintain your sexual health and well-being. We offer confidential testing and treatment for a range of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) including chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis, and HIV. Early detection and treatment of STIs are crucial for maintaining sexual health.
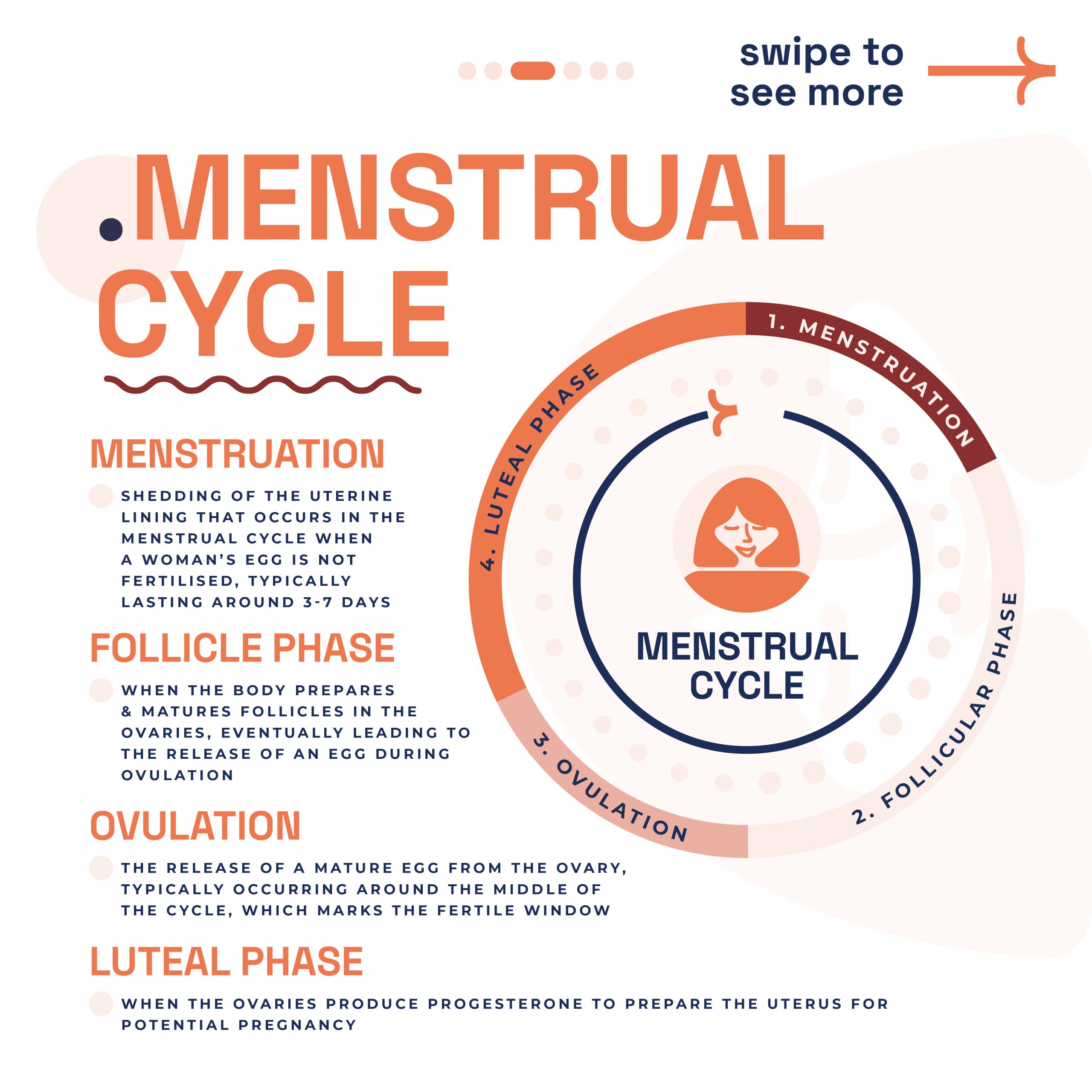
Spital Clinic offers a full range of contraceptive options including condoms, the pill, the patch, the ring, the implant, the IUD, and the IUS. Our GPs provide advice on the best contraceptive method for your needs and lifestyle. Their specialist GPs offer personalised advice on sexual health topics such as healthy relationships, safer sex practices, and sexual dysfunction. This is done to support you in maintaining a healthy and fulfilling sexual life. Routine cervical screening tests are essential for detecting abnormal cervical cells that could lead to cervical cancer if not treated. GPs can provide regular Pap smears to monitor your cervical health and catch any issues early.
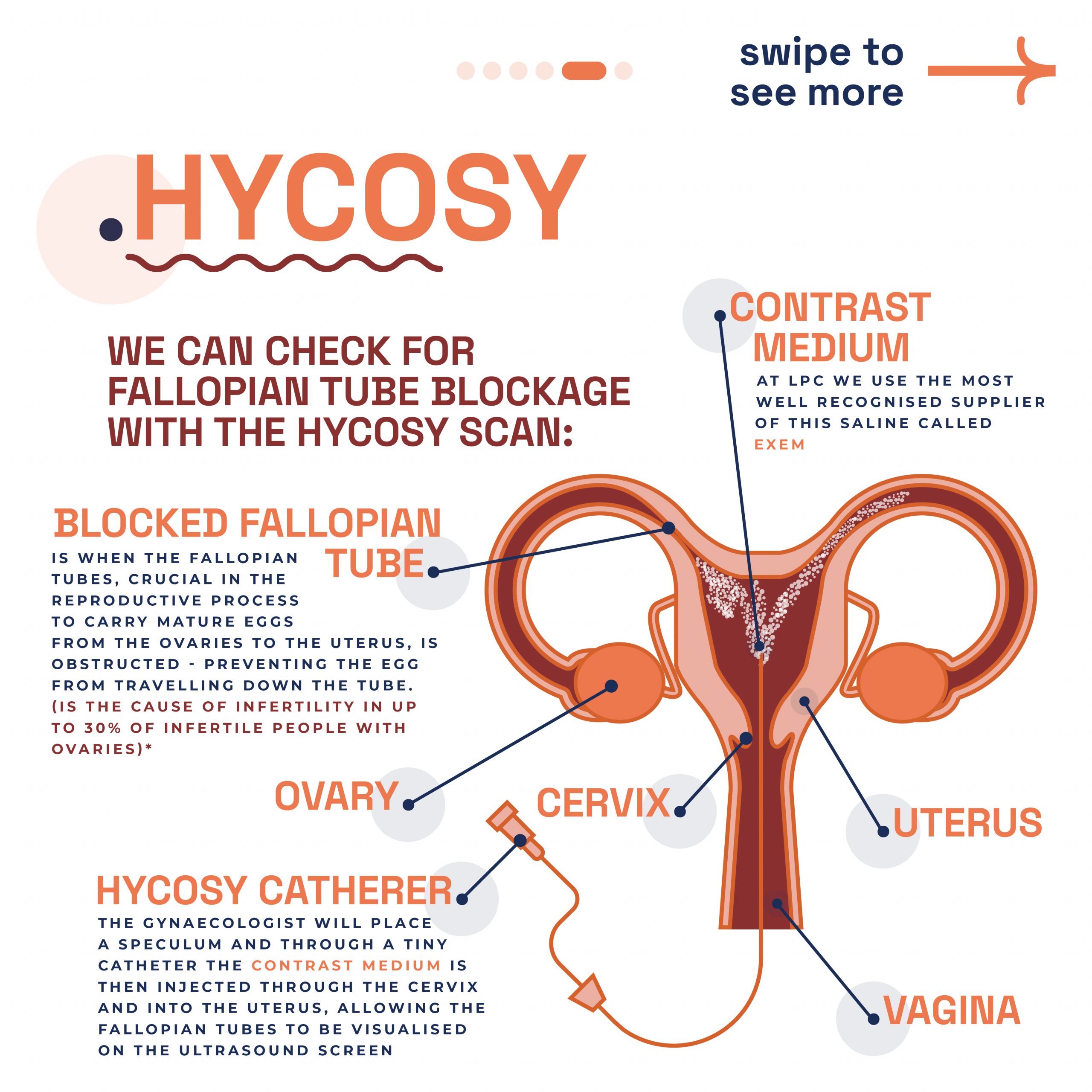
LPC on the other hand can offer pregnancy testing services and provide referrals for further care, including antenatal services, pregnancy ultrasound or Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT). This way our team and Spital Clinic’s GPs support you through every step of your pregnancy journey.
Women’s Health GP Services
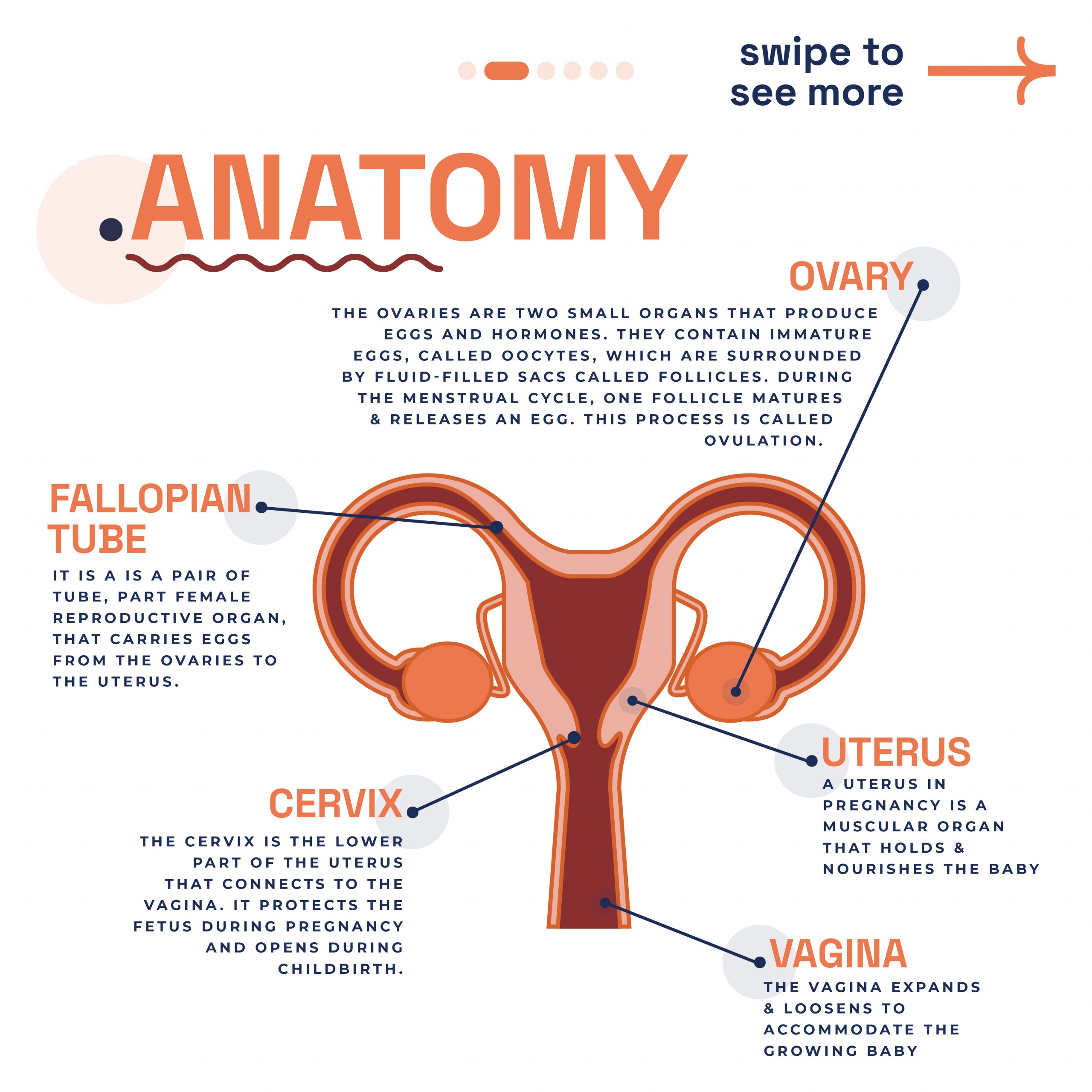
Women’s health is a key focus at Spital Clinic. Their female GPs have specialised expertise in women’s health, offering personalised care for various concerns. Spital is committed to providing comprehensive women’s health services in a supportive and compassionate environment. Regular gynecological check-ups are crucial for preventive healthcare. Their Women’s health GPs perform annual exams to monitor your reproductive health and detect any health issues early.
Menopause can be a challenging time for many women. Our GPs provide assessments and advice for managing menopausal symptoms, offering personalised care to help you navigate this stage of life with ease. We offer initial assessments and referrals for pregnant women, ensuring you receive the best care from the early stages of pregnancy. We provide support and guidance to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Our GPs address a variety of other women’s health concerns, including issues related to thrush, fertility, and more. Our team is equipped to handle a wide range of women’s health needs professionally and compassionately.
London Pregnancy Clinic Role
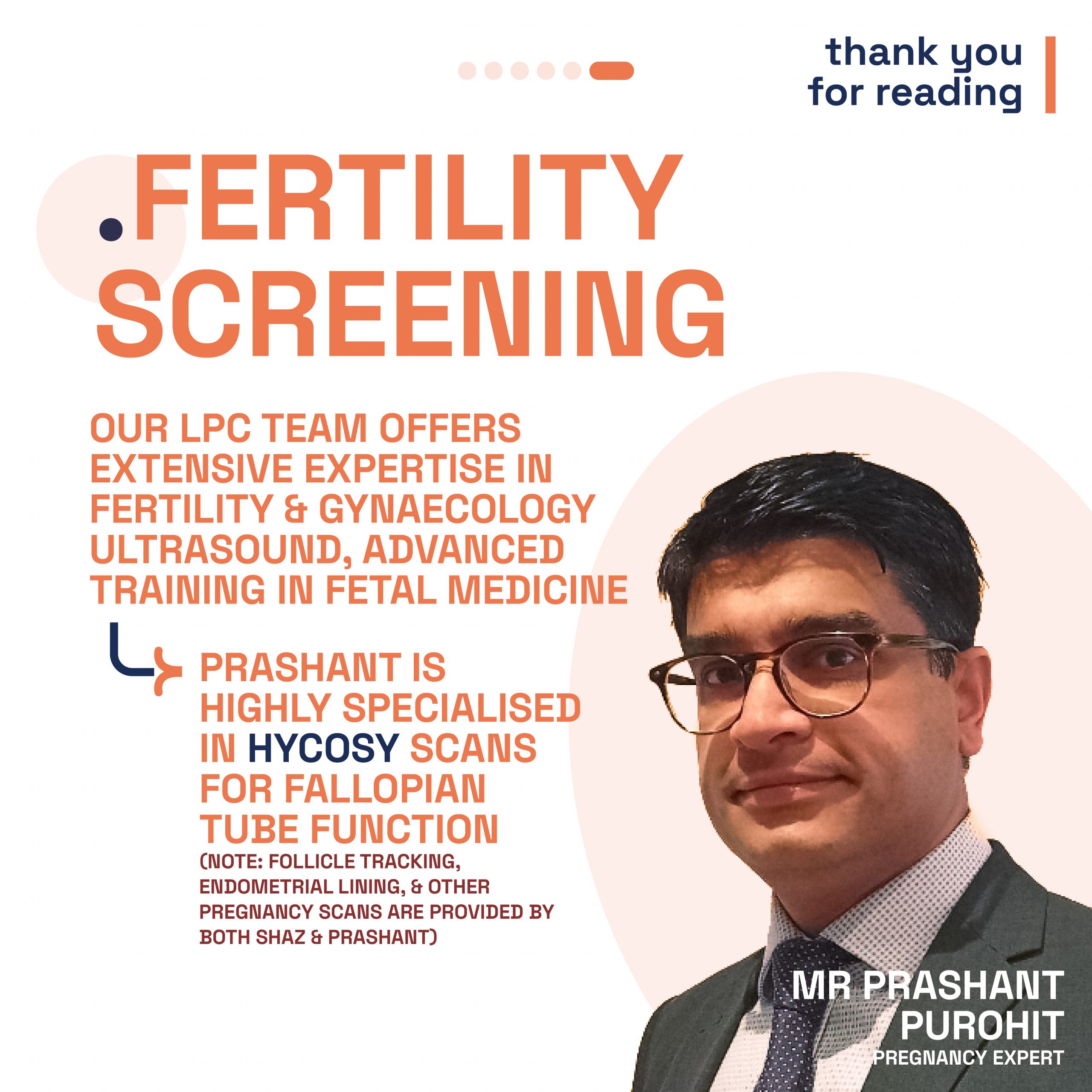
London Pregnancy Clinic supports Spital Clinic by providing specialised pregnancy, fertility, and gynecological services. This collaboration ensures that patients receive the highest standard of care throughout their healthcare journey.
Our team includes obstetricians, fetal medicine specialists, and midwives. We support you through every stage of pregnancy, from initial assessments to postnatal care. Our services include pregnancy scans, maternal medicine packages, and NIPT blood tests. We offer comprehensive fertility services to support your journey to parenthood, including fertility assessments, treatment plans, and ongoing support. Our team is dedicated to helping you achieve your fertility goals.
Our gynecological services cover a wide range of needs, including routine check-ups, treatment for gynecological conditions, and specialised care. We provide personalised care to ensure your health and well-being.
Why This Partnership is Important
This partnership is a significant step in our journey to offer holistic care. By combining our expertise, we provide comprehensive services that address all aspects of health. This ensures that our patients receive the best possible care at every stage of life. Holistic care means looking at the whole person, not just their symptoms. Our partnership allows us to provide integrated care that considers all aspects of health. This approach ensures better outcomes and a higher quality of life for our patients.
The collaboration with Spital Clinic enhances our service offerings. We can now provide more comprehensive care, from general practice to specialised women’s health services. This means our patients have access to a wider range of services in one convenient location. Our combined team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing the best care possible. By working together, we ensure that our patients receive high-quality, personalised care tailored to their needs.
Located conveniently in the heart of the City of London, Spital Clinic offers easy access to comprehensive healthcare services. This partnership ensures seamless continuity of care, with all necessary information securely managed and shared between our facilities.
Final Thoughts
We believe this partnership will significantly enhance our ability to provide high-quality, accessible healthcare. Whether you need a GP for general health concerns, sexual health services, or specialised women’s health care, Spital Clinic and London Pregnancy Clinic are here to support you. For more information about our services and to book an appointment, please visit Spital Clinic GP or contact our friendly staff.