Genetic Counselling Services Launch

Genetic Counselling Services Launch
Discover the importance of Genetic Counselling before and during pregnancy.
-
Published
-
Last Modified
Tags
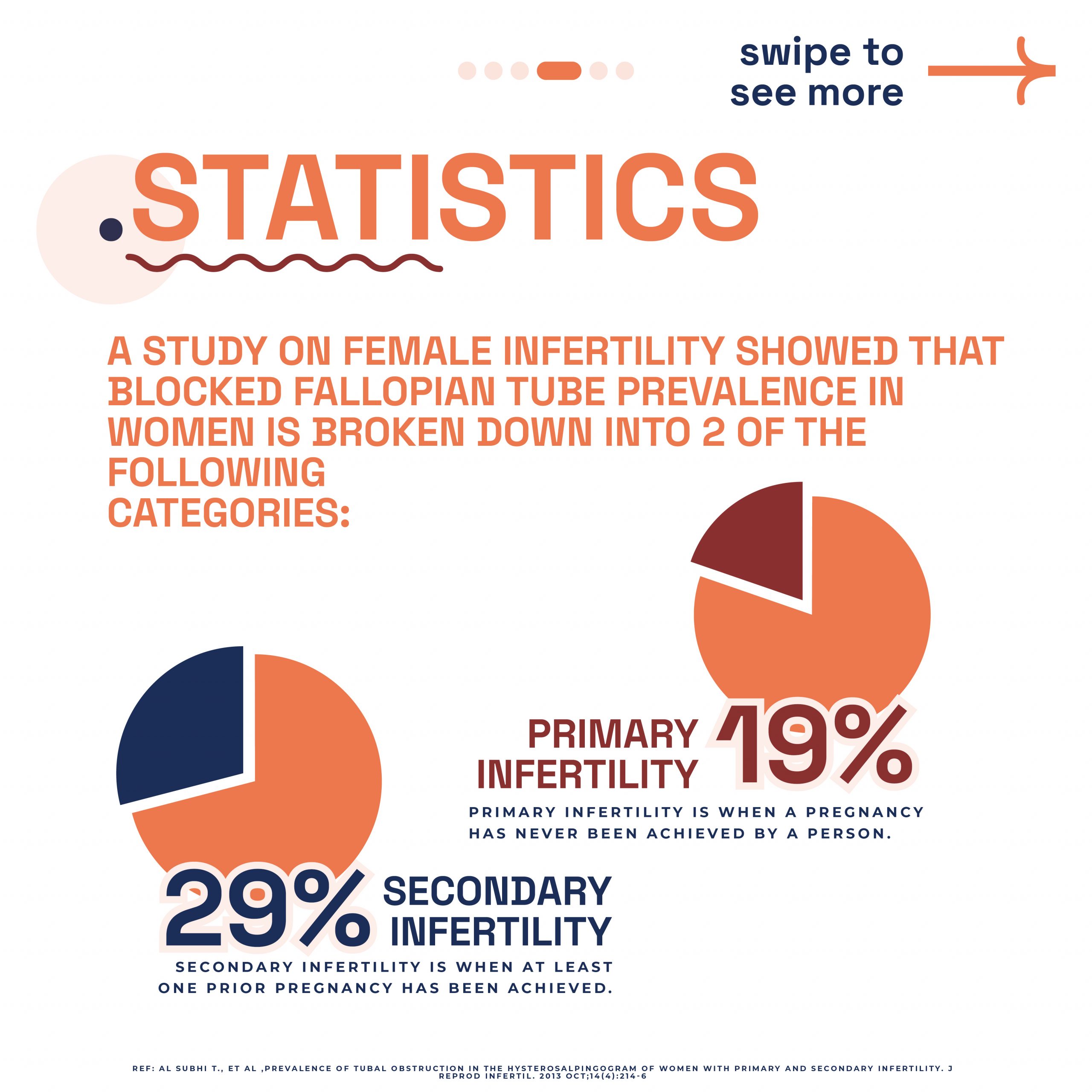
London Pregnancy Clinic proudly announces the launch of our new genetic counselling services. These services focus on reproductive genetic carrier screening. Our goal is to provide vital information to individuals and couples about their genetic risks. This information helps them make informed reproductive decisions aligned with their values and beliefs.
-

-
We are excited to introduce genetic counselling services at London Pregnancy Clinic. These services aim to help prospective parents understand their genetic risks. Genetic counselling is crucial in modern prenatal care. It offers both pre-test and post-test support, guiding you through complex genetic information.
Additionally, we are delighted to welcome Ms Ailidh Watson, our new genetic counselling specialist, to our team. Ailidh brings a wealth of experience and expertise in genetic counselling, particularly in prenatal care and patients with cleft lip and/or palate.
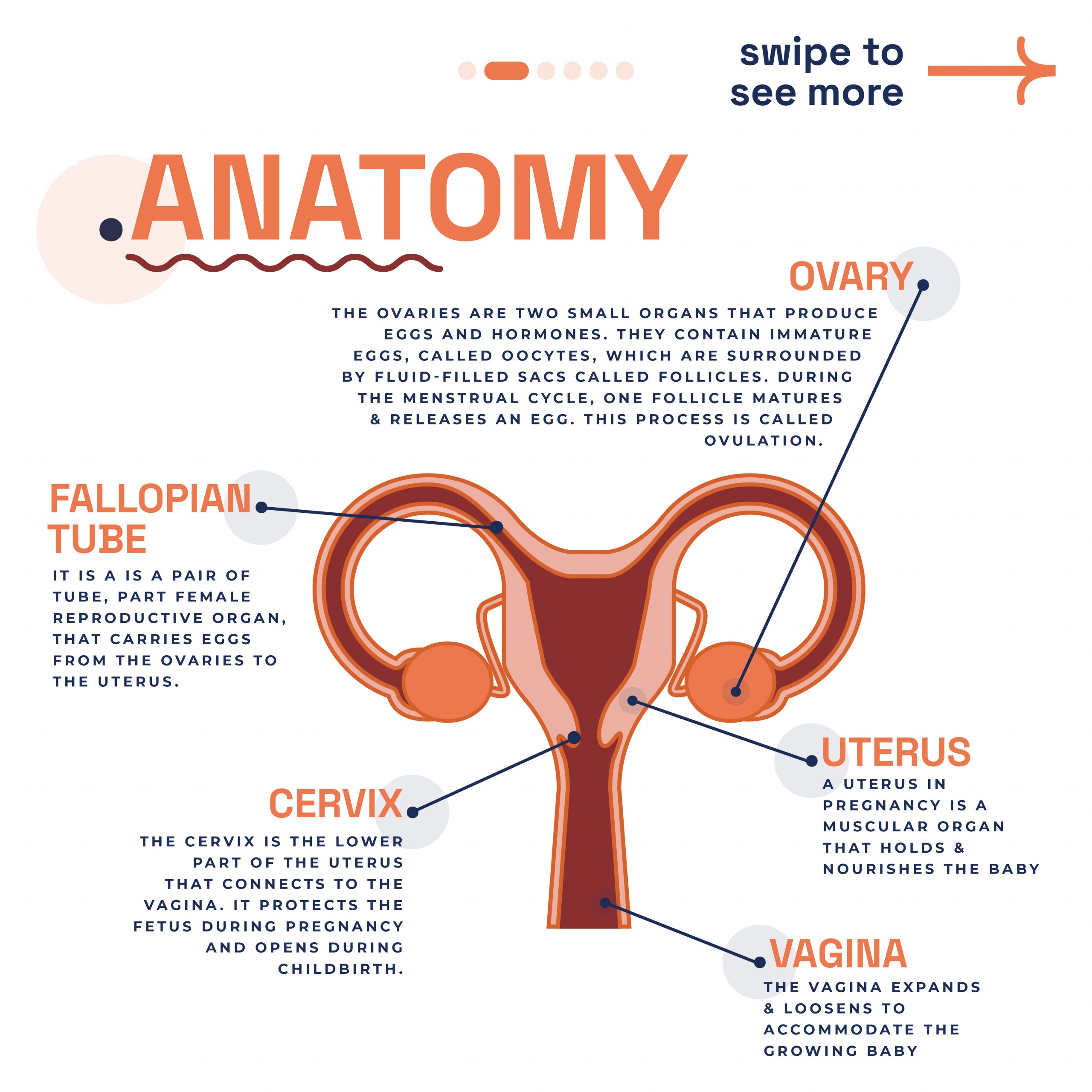
Genetic Testing We offer
At London Pregnancy Clinic, we offer a range of advanced genetic tests. These tests provide crucial information about your reproductive health. Here are the key tests we provide:
SMART Test: Our SMART Test NIPT is the most advanced non-invasive prenatal test and scan package in the world. This signature test gives parents detailed knowledge about their baby’s health without the risks of invasive testing. We offer two genetic packages: SMART Test KNOVA, performed by the leading US lab Fulgent, and SMART Test Genoma, performed by the top European lab Eurofins. Genetic counselling before the SMART test is essential to understand its advantages and limitations, ensuring you make an informed decision about your baby’s health.
Basic NIPT: The Basic NIPT is another non-invasive prenatal test we offer. It focuses on detecting the most common chromosomal abnormalities, including Down syndrome. Like the NIPT Smart Test, it uses a simple blood draw from the mother. This test is an excellent option for those seeking essential genetic information. With its high accuracy, it ensures peace of mind during pregnancy.
Carrier Screening: Our comprehensive carrier screenings identify if you or your partner are carriers of specific genetic disorders. This test covers a wide range of conditions, including cystic fibrosis and spinal muscular atrophy. Knowing your carrier status helps in planning for a healthy pregnancy. It allows you to explore reproductive options like IVF with preimplantation genetic testing (PGT). Moreover, carrier screening informs family members about potential genetic risks.
It’s important to distinguish between Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) and carrier screening:
- NIPT: Performed during pregnancy, typically between 10-20 weeks. It screens the fetus’s DNA for chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome.
- Carrier Screening: Tests the parents’ DNA for specific gene mutations that could be passed to their child. It can be done before or during pregnancy.
Benefits of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing offers several advantages, not just for you but for your entire family. Here are some key benefits:
Understanding Health Risks: Genetic testing identifies if you or your partner carry genes for specific genetic conditions. This understanding helps assess the risk of passing these conditions to your children.
Informed Decisions: Knowing your genetic risks allows you to make informed choices about pregnancy and family planning. You can consider options like IVF with preimplantation genetic testing (PGT-M), early interventions, or other preventive measures.
Personalised Care: With detailed genetic information, doctors can provide more personalised care. They can recommend specific tests, treatments, or lifestyle changes to help manage or reduce health risks.
Family Health Insights: Genetic testing reveals crucial health information that may affect other family members. If a genetic condition is identified, relatives can also get tested and take steps to manage their health.
Early Intervention: Detecting genetic conditions early leads to timely interventions and better management. This approach improves the quality of life for affected individuals.
Peace of Mind: For many, genetic testing provides peace of mind. Knowing your genetic information can alleviate uncertainties about potential health risks.
Preventive Measures: Genetic testing enables preventive measures, potentially reducing the risk of having a child with a genetic syndrome.
Overall, genetic testing empowers you with knowledge about your health and your family’s health. It helps you make well-informed decisions and take proactive steps. This ensures the best possible outcomes for you and your loved ones.
Impact on Family Planning?
Our carrier screening tests identify carriers of specific genetic disorders. Even without symptoms, you might still be a carrier. This knowledge is crucial for informed family planning. Knowing your carrier status can significantly influence family planning decisions. Couples who are both carriers face a 25% risk of having an affected child. This information empowers them to explore various reproductive options, such as:
- Using donor gametes to conceive.
- Pursuing in vitro fertilisation (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing (PGT).
- Accepting the risk and preparing for a potentially affected child.
- Considering adoption or remaining childless.
Carrier results can also influence the timing of pregnancy, prenatal testing decisions, early intervention for certain conditions, and emotional preparedness. Carrier screening identifies carriers for many genetic conditions, including:
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
- Sickle Cell Disease
- Tay-Sachs Disease
- Fragile X Syndrome
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Other conditions include Thalassemias (alpha and beta), Familial Dysautonomia, Fanconi Anemia, Gaucher Disease, and Niemann-Pick Disease.
Importance of Genetic counselling
Genetic counselling is vital in the carrier screening process. Our certified clinical genetic counsellors are dedicated to supporting you through every step. Here’s how:
Educating the Public and Healthcare Professionals: We provide standardised education about genetic carrier screening. This knowledge empowers you and your healthcare providers with essential information.
Pre-Test Counselling: Before testing, we outline the screening process and potential outcomes. This preparation ensures you are fully informed and ready.
Post-Test Counselling: After testing, we interpret your results and discuss your options. This support helps you understand your situation and make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
Collaborating with Healthcare Providers: Our counsellors work with other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive care in complex cases. This collaboration enhances your overall care experience.
In summary, London Pregnancy Clinic’s genetic testing and genetic counselling services offer comprehensive support and essential information. These services empower you to make informed decisions and take proactive steps for your family’s health. For more information or to schedule a test, please visit our website or contact us directly. Our team is here to support you in planning a healthy future for your family.
Ethical and Emotional Support:
Final Thoughts
London Pregnancy Clinic’s genetic counselling services represent a comprehensive approach to reproductive health. These services combine advanced genetic testing with expert counselling tailored to individual needs. They empower couples with the knowledge to make informed reproductive choices aligned with their values and circumstances.